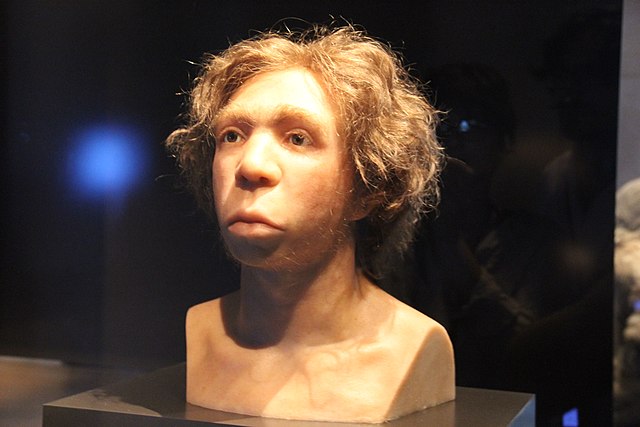
From the depths of prehistory, a fascinating tale unfolds—a story of an ancient species, the Neanderthals, who once roamed the Earth alongside our ancestors. While these primeval cousins have long since vanished from the face of the Earth, their DNA quietly persists within us, carrying fragments of their legacy. Modern humans, you and I, bear the genetic footprints of these long-extinct beings. In fact, some individuals possess as much as three to five percent Neanderthal DNA in their genes today, providing us with a remarkable connection to our distant past.
Genetics of Neanderthals
The Neanderthals, a species closely related to Homo sapiens, thrived in various regions of Europe and Asia roughly 400,000 to 40,000 years ago. These early humans had a robust build, with strong facial features and a distinct presence. They were skilled hunters and gatherers, adept at navigating their environments and adapting to the challenges of the prehistoric world.
Interbreeding between Neanderthals and Modern Humans
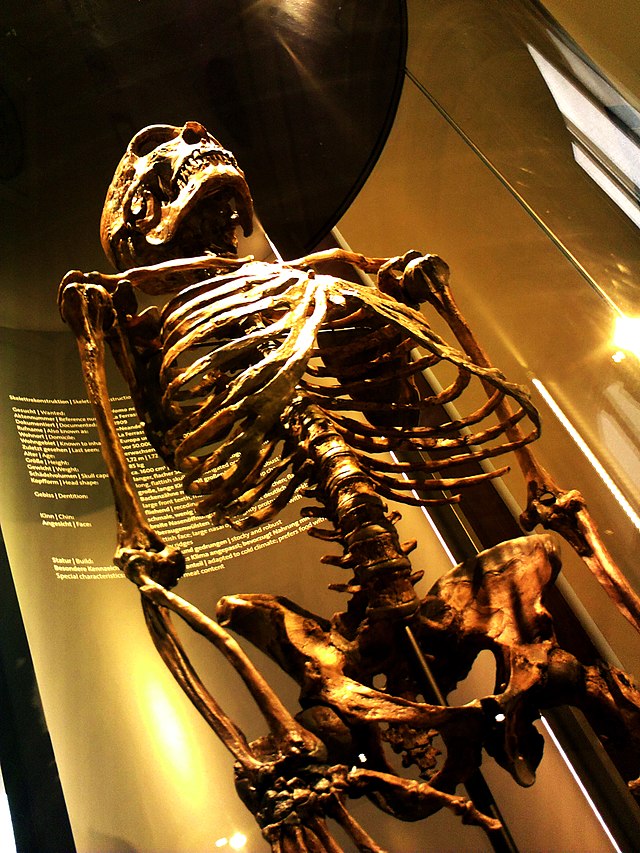

Genetic research has revealed a remarkable revelation: our ancient human ancestors, Homo sapiens, interbred with Neanderthals. By analyzing the genomes of modern humans, scientists have identified traces of Neanderthal DNA, confirming that interbreeding occurred thousands of years ago. This discovery highlights our shared genetic heritage and the intimate connection we have with our Neanderthal cousins.
Neanderthal DNA in Modern Humans
The presence of Neanderthal DNA in modern humans has been a subject of significant scientific interest and research. Studies have revealed that individuals of non-African descent carry traces of Neanderthal genetic material within their own genomes. This interbreeding between early Homo sapiens and Neanderthals, who lived in Eurasia before becoming extinct around 40,000 years ago, has left a lasting impact on the genetic makeup of modern humans.
Genome Sequencing of Neanderthals
One groundbreaking advancement in understanding the interbreeding between Neanderthals and early humans was the successful sequencing of the Neanderthal genome. In 2010, an international team of scientists extracted DNA from Neanderthal bones and reconstructed a draft genome. This achievement provided invaluable insights into the genetic similarities and differences between Neanderthals and modern humans.
Extent of Neanderthal DNA in Modern Humans
Subsequent studies have demonstrated that individuals of non-African descent carry approximately 1-2% Neanderthal DNA in their genomes. This percentage varies slightly among individuals, suggesting that interbreeding occurred at different times and locations. In contrast, individuals of African descent have little to no Neanderthal DNA, indicating that interbreeding was limited primarily to regions outside of Africa.
Influence on Modern Human Traits
Researchers have been able to identify specific regions of the human genome where Neanderthal DNA is more prevalent. These segments are associated with various traits and characteristics found in modern humans, including skin color, hair type, immune system response, and susceptibility to certain diseases. The intermixing of genetic material between Neanderthals and early humans likely contributed to the adaptation and survival of our ancestors in different environments.
Evolutionary Significance
The presence of Neanderthal DNA in modern humans highlights the complex interplay between different human species in our evolutionary history. The interbreeding between Neanderthals and early humans not only provided genetic diversity but also introduced advantageous genetic variants that have persisted in the human population over time. The incorporation of Neanderthal DNA into the modern human genome underscores the intricate web of genetic heritage that connects us to our ancient relatives.
Implications of Neanderthal DNA
The influence of Neanderthal DNA on modern humans is a subject of ongoing scientific investigation. Researchers have identified correlations between Neanderthal DNA and various traits, such as skin and hair characteristics, immune system responses, and susceptibility to certain diseases. This intermingling of genetic material has had both positive and negative implications for our species.
The presence of Neanderthal DNA in our genetic makeup has contributed to the diversity of human traits. It has allowed us to adapt to different environments and develop unique characteristics. However, it has also been associated with an increased risk of certain health conditions. This genetic legacy is a double-edged sword, bringing both advantages and challenges.
Genetic Legacy: Perplexity and Burstiness
The concept of perplexity and burstiness in genetics offers insights into the presence of Neanderthal DNA in modern humans. Perplexity refers to the level of uncertainty or complexity in our genetic composition, while burstiness describes the occasional occurrence of genetic bursts or episodes of significant change.
Neanderthal DNA adds to the perplexity of our genetic makeup by introducing a distinct genetic lineage into the mix. This interbreeding event acted as a burstiness factor, injecting novel genetic material into the evolving human genome. The result is a mosaic of genes and traits that make each of us unique.
The Importance of Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity plays a crucial role in the survival and adaptation of species. The interbreeding between Neanderthals and modern humans enriched our genetic pool, increasing the potential for genetic variation. This diversity has facilitated our ability to adapt to different environments and challenges throughout history.
Neanderthal DNA acts as a reservoir of genetic diversity, providing a range of genetic material that has contributed to the survival and success of our species. It serves as a testament to the intricacies of our evolutionary journey and the interconnectedness of all life forms.
Neanderthals: A Fascinating Piece of Our History
Beyond their genetic legacy, Neanderthals hold a captivating place in our cultural and historical narrative. Their existence sparks our curiosity, fueling a desire to comprehend our origins and the diverse paths our ancestors traversed. By studying Neanderthals and their DNA, we gain valuable insights into our own story as a species.
The presence of Neanderthal DNA in modern humans serves as a constant reminder of the depth and complexity of our shared past. It invites us to reflect on the extraordinary journey of life on Earth and the intricate tapestry of connections that bind us together.
Conclusion
The DNA of our primeval Neanderthal cousins courses through our veins, quietly weaving their story into the fabric of our own genetic makeup. While Neanderthals disappeared from the world long ago, their legacy persists within us, granting us a connection to our ancient past. Through scientific exploration and genetic research, we continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding our shared history, broadening our understanding of what it means to be human.



