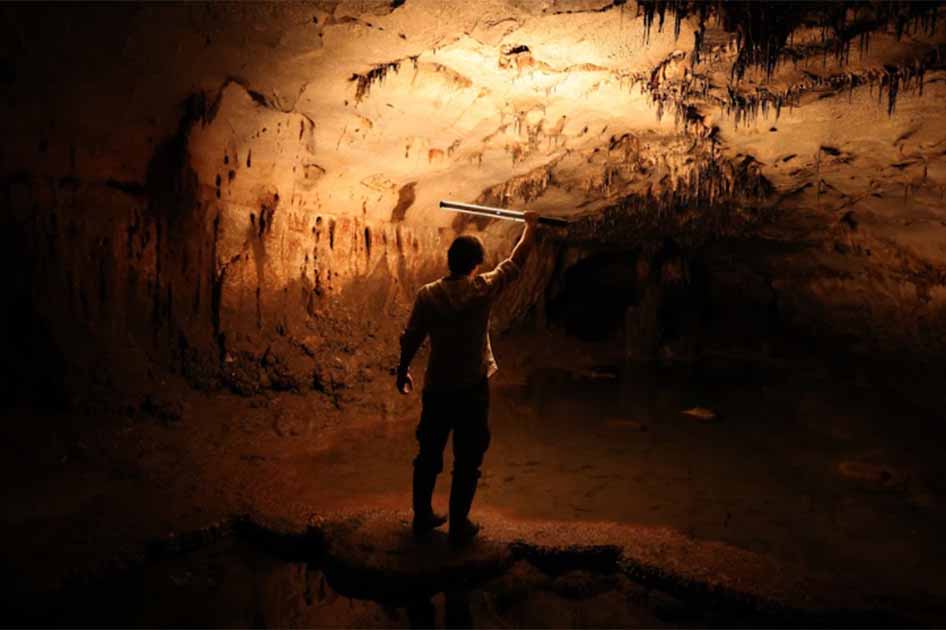
The world of archaeology recently witnessed a groundbreaking discovery as a team of experts from the Universities of Zaragoza and Alicante in Spain unearthed a hidden gem along the Eastern Iberian coast. Nestled in the heart of the province of Valencia, near the village of Millares, lies Cova Dones Cave, a cavernous wonder that has taken us on a mesmerizing journey back in time. In this article, we delve into the astonishing findings within this cave, where a wealth of ancient artwork dating back over 24,000 years has been revealed.
A Glimpse Into the Past

Cova Dones Cave is a vast underground complex, boasting numerous expansive caverns that extend up to an impressive 1,600 feet (500 meters) beneath the Earth’s surface. While explorers have been drawn to this mystical location since the 19th century, it wasn’t until 2021 that the cave’s secrets truly began to unfold.
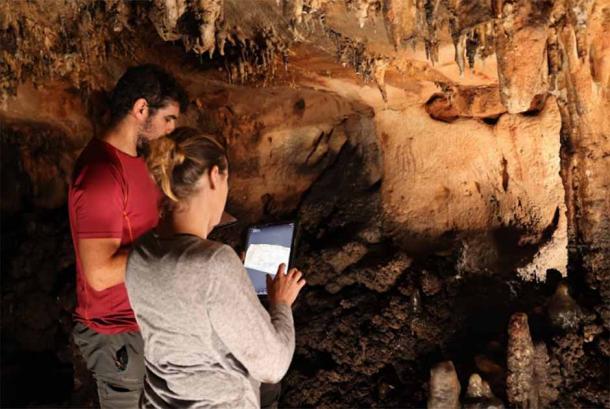
Spanish archaeologists Aitor Ruiz-Redondo, Virginia Barciela, and Ximo Martorell embarked on a remarkable journey into Cova Dones, unearthing a series of ancient artworks that had remained hidden for millennia. The initial discovery in 2021 revealed four faint images on one of the cave’s walls, delicately crafted using red clay sourced from the cave floor. This momentous revelation marked the beginning of a thrilling archaeological adventure.
Fast forward to 2023, and a more extensive survey of the site illuminated the presence of over 100 captivating images adorning the cave’s deep walls. These artistic wonders included a captivating fusion of animals and intricate geometric figures, a common choice among European cave artists of ancient times.
A Prehistoric Menagerie
The imagery discovered within Cova Dones Cave offers a captivating glimpse into the lives of our Paleolithic ancestors. Among the depictions are seven horses, seven hinds (female red deer), two aurochs, a stag, and two enigmatic unidentified animals. These creatures were not only essential for sustenance but also integral to the spiritual and cultural fabric of the time.
While the meaning of the geometric figures remains shrouded in mystery, some suggest a connection to ancient spiritual beliefs and the visionary experiences of shamans in altered states of consciousness. Dark caves, like Cova Dones, provided the perfect setting for such profound journeys, offering sensory deprivation conducive to altered states of mind.
A Palette of Red Clay
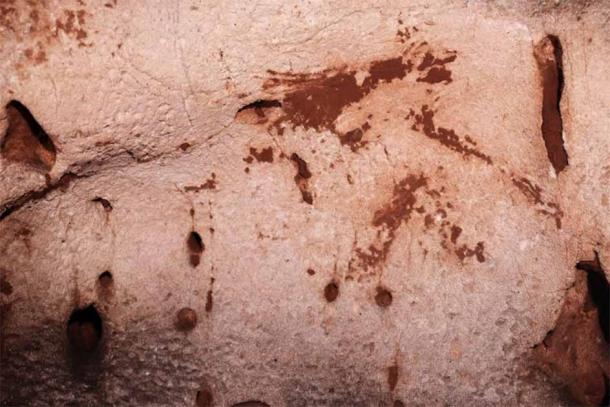

Intriguingly, more than 80 of these remarkable images were meticulously painted onto the cave walls, while the remainder were etched and engraved into the soft limestone. What sets Cova Dones apart is the choice of red clay for the paintings, deviating from the typical use of red ochre found in Paleolithic period cave art. This unconventional choice hints at the unique character of this ancient artistic haven.
Unveiling the Artistic Timeline
Dating these ancient masterpieces posed a challenge, but the enigmatic cave bears of Paleolithic Europe left their mark on the walls, offering vital clues. Scratch marks left by these now-extinct creatures overlapped with some of the finger flutings created by the cave artists. As the cave bear became extinct around 24,000 years ago, it serves as a crucial time marker, confirming that the cave paintings are at least as old.
Stylistically, the images and motifs found in Cova Dones closely resemble cave paintings elsewhere in Europe dated between 22,000 and 19,000 BC. This places these masterpieces within the middle years of the Upper Paleolithic, a time when extreme temperatures and droughts rendered much of western and northern Europe uninhabitable.
Redefining Geography and Culture
The significance of Cova Dones extends beyond its artistic richness; its precise geographical location challenges existing assumptions. While the majority of European cave paintings have been discovered in the Franco-Cantabrian region, eastern Spain has remained relatively uncharted territory for such findings. Cova Dones defies this norm, emerging as a treasure trove of ancient cave imagery, with over 100 images in its collection.
A Glimpse into Prehistoric Life
The gallery of images uncovered within Cova Dones stands as a testament to the complexity and diversity of ancient life. It rivals even Axturra, the only cave on the Iberian Peninsula to boast a comparable range of motifs. However, Axturra’s collection, discovered in 2015, comprises approximately 70 images dating back to around 12,500 BC, paling in comparison to the treasure trove of Cova Dones.
What’s most exciting about the ongoing archaeological work at Cova Dones is that it’s merely scratching the surface, quite literally. The cave’s vast expanse, reaching depths of nearly half a kilometer, conceals walls that remain unexamined for signs of ancient human activity. As researchers delve deeper into this labyrinthine wonder, it’s likely they’ll uncover generations of artists who used this sacred canvas to convey their beliefs and lifestyles.
In conclusion, Cova Dones Cave has rewritten the narrative of prehistoric art and culture in eastern Spain. Its extensive collection of ancient cave paintings and engravings, dating back over 24,000 years, is a testament to the enduring human urge to express and create. As the excavation continues, we anticipate even more astonishing revelations about the rich tapestry of life in this ancient world.
How did the cave artists create these ancient paintings in Cova Dones?
The artists primarily used red clay sourced from the cave floor to paint the images. Some were also etched and engraved into the soft limestone walls.
What do the geometric figures in the cave art symbolize?
The meaning of the geometric figures remains a subject of debate. Some suggest they may be linked to ancient spiritual beliefs and the experiences of shamans in altered states of consciousness.
Why is the choice of red clay significant in Cova Dones’ cave art?
Red clay was an unusual choice for the region, as red ochre was more commonly used in Paleolithic cave art. This choice adds to the uniqueness of Cova Dones’ artistic heritage.
How did researchers determine the age of the cave paintings in Cova Dones?
The age was estimated by studying the overlap between scratch marks left by extinct cave bears and finger flutings created by the cave artists. The extinction of cave bears around 24,000 years ago served as a key time marker.
What sets Cova Dones apart from other cave painting sites in Europe?
Cova Dones challenges the geographical distribution of cave art in Europe, as it is located in eastern Spain, a region less explored for such findings. It houses one of the most extensive collections of cave paintings and engravings on the continent.



