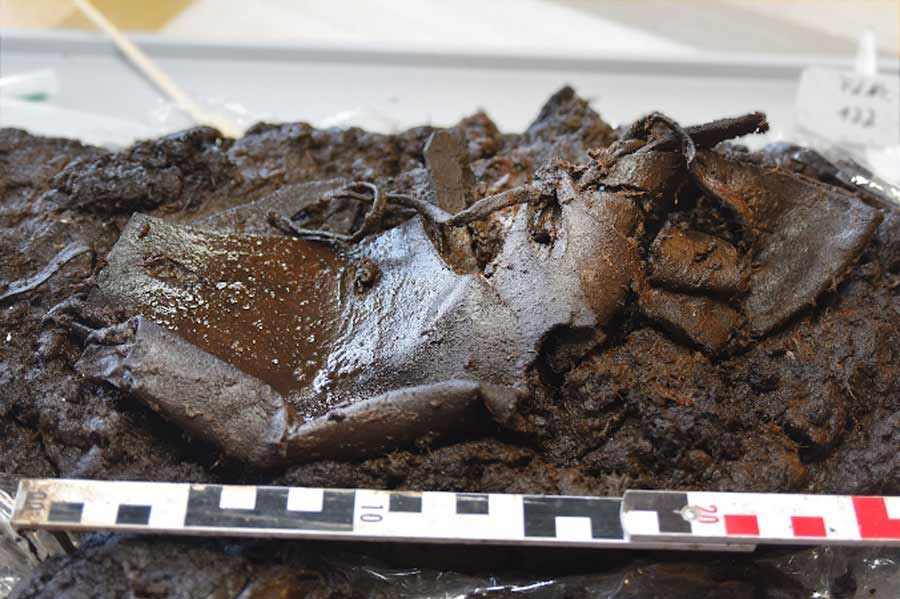
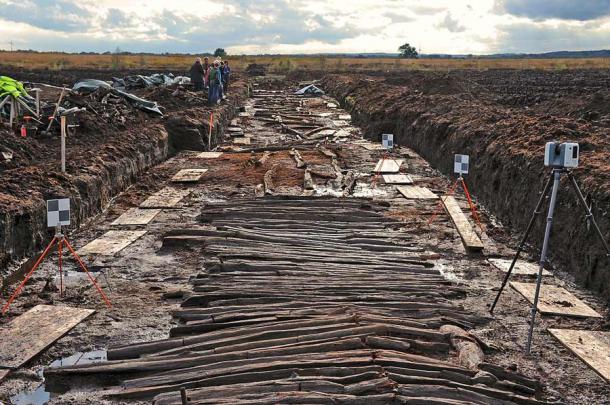
Bogs, those enigmatic landscapes shrouded in mystery, have often yielded unexpected treasures from the depths of time. From well-preserved human bodies to peculiar artifacts like barrels of butter, these marshy terrains hold secrets that unravel stories of ancient civilizations. In the heart of Lower Saxony, Germany, archaeologists have unearthed yet another marvel: a remarkably well-preserved leather artifact, a 2,000-year-old Ancient Shoe, nestled beside the remnants of a wooden road dating back to the Bronze Age.
Exploring the Ancient Relic: The Tale of the 2,000-Year-Old Shoe

This extraordinary find represents a sandal-like footwear, intricately crafted and secured with a strap, marking it as the oldest shoe discovered in the region. Unlike modern footwear churned out by industrial processes, this shoe bears the hallmark of meticulous craftsmanship, tailored to fit its wearer with precision, enduring the ravages of time.
Speculation surrounds the circumstances of its entrapment in the bog’s embrace. Perhaps lost amidst the treacherous terrain while its owner navigated a laden cart through the bog, the shoe found itself ensnared in the sticky mud, evading recovery. The discovery of a broken carriage axle nearby hints at the possibility of an unfortunate mishap, further complicating the narrative of its deposition.
Unveiling the Bronze Age Bog Trail
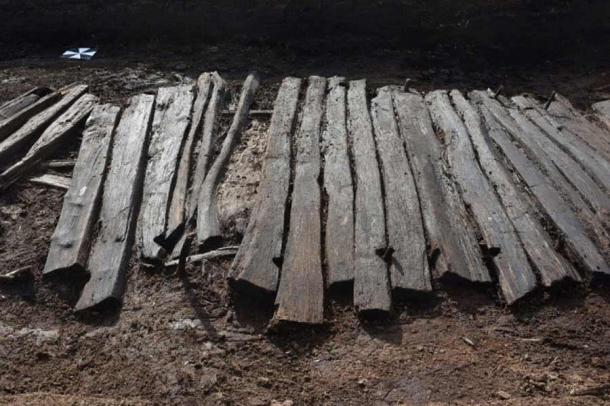

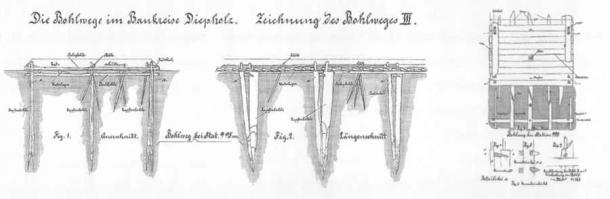
The excavation, spearheaded by the Lower Saxony State Office for Monument Preservation and Denkmal 3D from Vechta, Germany, sheds light on the historical significance of the site. The wooden road, believed to have been traversed by cattle-drawn carts, served as a vital artery connecting settlements across the bog-ridden landscape.
This region, steeped in history, bears witness to millennia of human activity, with over 500 such paths identified in Lower Saxony alone. Among these ancient routes, Bohlenweg Pr 6 emerges as a testament to ingenuity and perseverance, stretching over 4.2 kilometers and dating back to the late Bronze Age.
Preservation of History: The Role of Bogs
Lower Saxony’s Minister for Science and Culture, Björn Thümler, underscores the significance of bogs as custodians of our past. These marshlands not only preserve tangible artifacts but also offer glimpses into bygone eras, capturing moments frozen in time. The meticulous excavation of the bog path between 2019 and 2022 has unearthed a trove of organic relics, enriching our understanding of ancient civilizations.
The discovery of the 2,000-year-old shoe serves as a poignant reminder of the transient nature of existence. Despite the ebb and flow of time, this humble footwear endures, bearing witness to the lives lived centuries ago. While not the oldest shoe on record, its significance lies in its ability to bridge the gap between the past and the present, offering a tangible connection to our shared human heritage.


